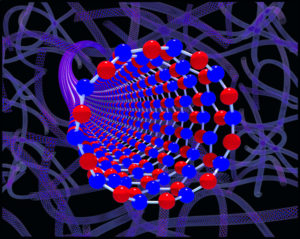
New Materials through SynthesisPhysical Science Centric Discipline “The manipulation of atoms and molecules to produce new materials. Includes the development of new synthetic techniques and methodology, and equipment modification and customization.” Academic Disciplines include Chemistry,Physics, Ceramics, Metallurgy, and Materials Science. Technologies are resins (solid and liquid), metal alloys, ceramic solid solutions, coatings, adhesives, nanomaterials, molecularly engineered materials, elastomers, “active/smart” materials. Products are powders, pellets, ingots, solutions, wafers and other stock forms of materials ready to be processed into test specimens. |
|
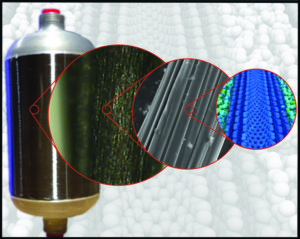
New Materials through ProcessEngineering Centric Discipline “The creation of new materials through the processing or combining of stock materials into new forms. Includes the development of new fabrication techniques and technology.” Academic Disciplines include Chemical, Ceramic, Polymer, Mechanical, and Metallurgical Engineering. Technologies are processing parameter control, novel fabrication methods, scalable processes, new hybrid materials, bonding and joining technology, extrusion/injection surface engineering and preparation, and equipment design and modification. Products are particulate, fiber and laminated reinforced composites, films, membranes, engineered surfaces, electrical, optical, and mechanical devices, and prototype structures. |
|
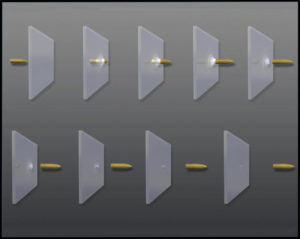
CharacterizationPhysics Centric Discipline “The analysis of material properties at scales from atomic through bulk. Includes instrument design, statistically based data reporting, and new test method development and validation.” Academic Disciplines include Chemistry, Physics, Microscopy, and Materials Science. Technologies are customized analytical equipment, unique property test-data sets, streamlining of verification procedures, forensic failure analysis, validation of new test methodologies. Products are highly accurate and precise data, quality specimen development, unique analytical methods, accurate lifecycle testing, and a fundamental understanding of material properties and composition as tied to synthesis and processing. |
|
ComputationNumerical Methods Centric Discipline “The use of computation to simulate and predict the behavior and interactions of materials from synthesis and processing through lifing. Includes the input of experimental data and the development of computational and process control algorithms.” Academic Disciplines include Computer Science, Physics, Mathematics, and Computer Engineering. Technologies are Interactive machine codes, database of experimental inputs and material properties, reduction in the amount of experiments to develop a new material or validate a result. Products are faster development of new materials, process control algorithms, faster computational methods, increased predicative lifing capabilities, and the development of a Virtual lab. |